

















September 2025
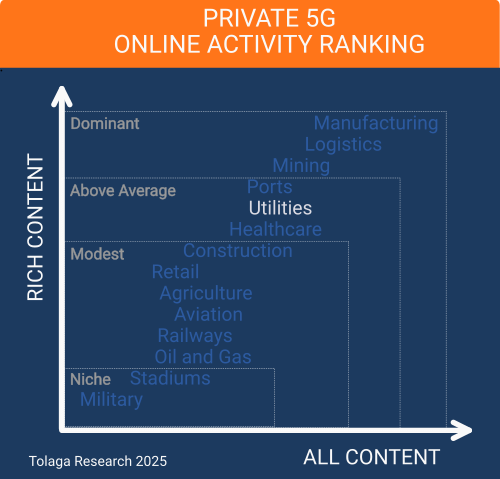
The utilities industry vertical provides above-average opportunities for the Private 5G (P5G) market, with our online content survey ranking utilities 5th out of the 14 industries researched.
Ericsson and Nokia are leading the online narrative for P5G deployments with utilities to deliver secure, high-performance connectivity that enhances grid modernization, automation, and operational efficiency, while supporting critical applications such as outage detection, smart metering, remote monitoring, and integration of future energy. technologies.
Leading real-world deployments so far are concentrated in the electricity sector, supporting applications such as smart metering, grid automation, remote inspections, and distributed energy integration.
Multi-service (electric, gas, and water) P5G deployments are rare, with the gas and water sectors lagging behind the electric industry.
Significant barriers include high upfront costs, complex legacy system integration, cybersecurity risks, and regulatory hurdles, requiring utilities to adopt a phased, pilot-driven approach, build strong vendor partnerships, and invest in workforce upskilling.
Ultimately, successful P5G adoption depends on demonstrating clear value through targeted use cases, fostering cross-functional and cross-industry collaboration, and prioritizing compliance, security, reliability, and scalability from the outset.
The utilities sector encompasses companies and services that provide essential infrastructure for daily living and economic stability, primarily through the delivery of electricity, natural gas, and water.
Digital transformation across energy, water, and natural gas utilities is driven by the need to modernize aging infrastructure, enhance operational efficiency, and improve service reliability, whether through integrating renewable energy and smart grids in electricity, deploying IoT sensors and smart meters for leak detection and billing accuracy in water systems, or utilizing predictive analytics and digital twins for pipeline monitoring and safety in the gas sector. Rising customer expectations for seamless digital services, tightening environmental and regulatory requirements, and the imperative to leverage real-time data analytics for better asset management and compliance further accelerate this shift, while the growing threats of cyber and cyber-physical attacks and climate change, combined with the opportunities provided by cloud computing and AI, drive utilities in all three sectors to embrace advanced technologies for greater resilience, sustainability, innovation, and superior customer engagement.
Utility companies are exploring Private 5G (P5G) networks to improve reliability, enhance cyber and cyber-physical security, and gain greater control over increasingly complex and distributed systems. These systems often require low-latency, high-bandwidth, and continuous connectivity for functions such as grid and pipeline monitoring, automated meter reading, leak detection, and remote field operations. Compared to public or legacy networks, P5G offers dedicated infrastructure that can be owned and configured to meet specific requirements. While adoption remains early, P5G shows potential to support secure IoT deployments, enable advanced analytics, and streamline communication systems, offering possible cost efficiencies and operational improvements over time.
Online content published since 2022 that related to P5G for the utilities industry was collected and filtered using proprietary web crawling, AI, and NLP tools, yielding a corpus of 214 relevant impressions (ALL CONTENT). Of this, 194 focused on company activity in the sector (RICH CONTENT), identifying 178 companies. Approximately 31.0 % of the content in the corpus referenced multiple industry verticals in addition to utilities, with an average of between 2 and 3 other industries mentioned in this content.
The chart below compares the content corpus for P5G for the utilities industry against other industry verticals to gauge relative market momentum. The analysis indicates that the utilities industry currently brings above-average opportunities for P5G relative to other vertical market segments.
Natural language processing (NLP) and AI tools were used to identify companies mentioned in the content corpus, measure their prevalence (BREADTH), and evaluate how frequently they appear alongside other companies (DEPTH). Of the 178 companies identified, the ranking of the top 10 is shown in the chart below.
Ericsson is actively advancing 5 G solutions for the utilities sector, providing tailored solutions for critical infrastructure such as power plants, substations, and offshore wind farms. Their approach includes simplifying 5G network deployment and management with AI-driven operations, seamless provisioning, and unified policy control. Ericsson collaborates with partners like OneLayer to integrate zero-touch, zero-trust network access solutions that enhance device and SIM onboarding, network security, and operational efficiency for utilities. These innovations help utilities meet automation, safety, and sustainability goals while ensuring reliable, scalable wireless coverage indoors and outdoors, complementing or replacing Wi-Fi and other legacy systems for digital transformation across their operations.
Nokia is deploying private 5G networks for utilities to modernize grids, improve outage detection and restoration, and enhance operational efficiency. Their solutions provide secure, reliable connectivity for critical tasks like automated meter reading, grid monitoring, and fault detection, supporting future technologies such as electric vehicles. Notably, Nokia is building the first full-scale standalone private 5G network for Memphis Light, Gas, and Water, enabling faster communication during storms or cyber events and boosting automation and smart control. Their technology integrates with existing infrastructure and modern IoT devices, helping utilities accelerate digital transformation with scalable, secure wireless networks.
NLP and AI techniques were used to identify and classify keywords and phrases in the content corpus into 27 topics. Their frequency was measured (BREADTH) and their inter-relationships analyzed (DEPTH). The chart below shows the top 10 topics.
The most prominent topics in online content today are compute and communications, security, smart grid, and field area networks. Over time, we expect themes such as renewables and remote operations to increase in prominence.
Utility companies are deploying P5G for a wide range of use cases to support their modernization efforts, including network consolidation, advanced field monitoring and communications, smart metering, outage detection, automated grid management, and integration. Several notable use cases are identified below.
MLGW serves 440,000 customers in the Memphis and Shelby County area, making it the largest three-service municipal utility in the United States. In July 2025, it announced a contract with Nokia to deploy a standalone P5G network. The deployment is intended to unify communications across its electric, gas, and water services, supporting critical applications such as automated meter reading, grid monitoring, fault detection, and remote field operations. MLGW also aims to reduce outages, accelerate service restoration, and fortify its grid modernization efforts.
SCE is one of the largest electric utilities in the United States, serving over 15 million people across central, coastal, and Southern California. In November 2024, SCE deployed a P5G Field Area Network (FAN) with Nokia equipment operating in the Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) spectrum. This is the first P5G-FAN network in the United States, and aims to improve grid reliability, safety, and operational efficiency by enabling real-time fault detection, remote diagnostics, and enhanced field crew communication. The FAN also supports the secure integration of distributed energy resources, such as solar and storage, helping SCE advance its grid modernization and carbon-neutral goals.
Électricité de France (EDF) has deployed private LTE and P5G networks across its nuclear power plants to enhance operational safety, efficiency, and reliability. In May 2024, EDF announced plans to expand its private LTE infrastructure in partnership with Ericsson and Thales, while also pursuing trials of P5G as part of a long-term network upgrade strategy. Although LTE remains the operational backbone, EDF is actively trialing P5G use cases, including drone-based inspections, real-time video, augmented reality, and edge computing, using experimental licenses and collaborating with partners such as Ericsson, Thales, and Sequans.
In 2024, ČEZ’s Temelín Nuclear Power Plant in the Czech Republic announced the deployment of a private 5G (P5G) network in partnership with Vodafone. Designed to operate independently from public networks, the system aims to provide greater control and security for site communications. It replaces traditional walkie-talkies with digital voice services and introduces support for tools such as augmented reality (AR) in maintenance and inspection tasks. The network’s bandwidth and latency capabilities enable connectivity to IoT sensors and monitoring devices, with the goal of improving equipment oversight and enabling predictive maintenance. As a pilot project, it will help ČEZ evaluate the feasibility and value of wider P5G adoption across its infrastructure, particularly in terms of operational safety, efficiency, and system integration within a nuclear setting.
China's State Grid Corporation (SGCC), the world's largest state-owned electric utility, operates the majority of China’s power transmission infrastructure and serves over 1.1 billion people across 26 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities. Since 2021, SGCC has been rolling out a large-scale P5G network, starting in Shandong Province and expanding in 2023 to Gansu Province. The Shandong deployment, featuring over 30,000 base stations, was developed in collaboration with China Unicom, Huawei, and TD Tech. It leverages network slicing on China Unicom’s infrastructure, including Reduced Capability (RedCap) slices to enable cost-efficient, low-power IoT connectivity. Notable use cases in Shandong include distributed photovoltaic (PV) control, grid automation, load balancing, and advanced metering. The Gansu network supports high-capacity use cases, such as real-time video surveillance, mobile inspection robots, and other 5G-enabled devices that require dedicated bandwidth and low latency.
China Southern Power Grid (CSG) is the second of China's two giant state-owned electric utilities, responsible for power transmission and distribution to over 300 million people in five southern Chinese provinces. CSG has deployed an extensive P5G network for its smart grid operations, in partnership with China Mobile and Huawei. The P5G network operates a dedicated network slice on China Mobile's public network, used for mission-critical applications such as differential protection, phasor measurement, video surveillance, and inspection robots at substations to enhance automation, operational efficiency, and cost savings across CSG's service territory in southern China.
Kansai Power is Japan's second-largest electric utility, serving the Kansai region, including Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe, with a diversified mix of power sources. In 2022, Kansai Power deployed a P5G network to enable 5G-connected drones to conduct enhanced blade inspections and support maintenance operations at the Eurus Akita Port wind farm in Akita.
Korea Electric is South Korea's state-owned national electric utility, handling generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. In late 2022, Korea Electric launched a P5G network in partnership with Samsung Electronics at its Shin-Jungbu substation, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote inspection using IoT sensors, AI, and quadruped robots. The solution enhanced grid safety and operational efficiency, particularly for aging infrastructure. At the time of deployment, Korea Electric indicated plans to expand P5G across additional substations as part of its broader digital grid transformation strategy.
Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP) operates the Hanul Nuclear Power Plant, a major nuclear facility in South Korea, home to several operational reactors and additional units under construction. In December 2022, KHNP deployed P5G in partnership with HFR to support mission-critical functions, including resilient transmission equipment redundancy, emergency command and communications, and real-time, AI-enhanced situational awareness for disaster response.
Nobelwind is a 165 MW offshore wind farm off the Belgian coast, operating 50 turbines since 2017. In June 2024, Nobelwind offshore wind farm in the North Sea deployed a P5G network, upgraded from an earlier private LTE system through the 5G Seacurity project in partnership with Citymesh. The network supports real-time security monitoring by connecting drones, intelligent sensors, and autonomous vehicles, enabling rapid detection of and response to potential threats. The deployment is part of a broader North Sea security initiative, leveraging 5G's high capacity and low latency to transmit large volumes of data reliably and immediately for enhanced operational safety and site protection.
PGE is an Oregon-based electric utility serving nearly 900,000 customers. In January 2023, PGE in partnership with Expeto, commercially deployed a private wireless network spanning over 4,000 square miles across Oregon, connecting more than 250,000 grid elements, including smart meters, EV charging stations, and wildfire detection cameras, primarily by leveraging existing public LTE and 5G infrastructure from major carriers, managed and secured by Expeto's NeXtworking software platform. This software-defined, hybrid network model operates like an SD-WAN, pooling multiple carrier profiles onto PGE’s SIM cards and orchestrating private virtual connectivity over public cellular networks.
North Rhine-Westphalia water utility, Germany, is currently piloting a 5G solution for water infrastructure automation, leveraging public 5G network slicing in partnership with Siemens and Telefonica. This system utilizes Siemens' 5G routers at utility sites, with dedicated and secure slices of Telefonica’s public 5G network, to enable real-time, centralized monitoring and control of dispersed water assets, such as pumping stations and treatment plants. The deployment is still in the testing phase and has not yet been rolled out as a permanent, full-scale production system.
Most utilities face significant barriers to adopting P5G, including high upfront infrastructure costs, integration with legacy systems, and ensuring compatibility across devices and applications. Upgrading outdated or fragmented networks to P5G requires significant investment and careful planning, as underperformance can undermine confidence and delay broader rollout. Utilities must also navigate complex regulatory landscapes and rising cybersecurity threats that must be addressed in their P5G implementations. Additionally, effectively aligning P5G deployments with the utility’s operational needs, such as supporting distributed energy resources, real-time monitoring, and automation, can create technical, financial, and organizational hurdles that stifle progress.
To overcome these obstacles, utilities typically adopt phased, collaborative approaches focused on tangible outcomes. Starting with targeted pilots, such as substation automation, inspection drones, or distributed energy (DER) management, helps validate technology, build internal expertise, and demonstrate value. Strong vendor partnerships ease integration with legacy systems, while proactive regulatory engagement addresses spectrum and cybersecurity requirements. A “security by design” mindset enhances infrastructure protection, and cross-functional collaboration supported by executive sponsorship ensures alignment across technology, operations, and business priorities. With ongoing workforce training and a focus on interoperability and long-term planning, utilities can position themselves to unlock the full potential of P5G in modernizing the grid.